XX
Create your first page
First, we create the link between the URL and the Template. This is done with the View in shop/views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render
from django.views import View
from .models import Product
class Index(View): # will be used with "views.Index"
def get(self, request):
return render(request, 'shop_index.html', { # will look for shop/templates/shop_index.html
'products': Product.objects.filter(active=1) # see next chapter for ORM
})
Second, we have to set the URL. URLs are stored in {app_name}/urls.py so go ahead and create shop/urls.py:
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.Index.as_view(), name='shop_index'),
]
This URL has to be activated in {project_name}/urls.py, which is django_overview/urls.py in our case:
from django.urls import include, path
urlpatterns = [
path('', include('shop.urls')),
# ...
]
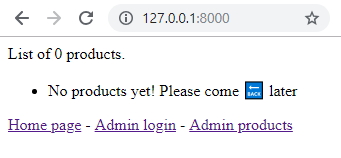
Finally, there’s the HTML template shop/templates/shop_index.html. Note: It’s always a good idea to prefix templates (here with shop_) or to put them in a subfolder (such as shop/index.html) because templates can be called from anywhere. So if you got multiple templates/index.html, you might end up with a weird mix.
List of {{ products|length }} products.
<ul>
{% for product in products %}
<li>{{ product.name }}</li>
{% empty %}
<li>No products yet! Please come 🔙 later </li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<a href="{% url 'shop_index' %}">Home page</a> - <!-- named url from shop/urls.py -->
<a href="{% url 'admin:index' %}">Admin login</a> - <!-- package url from contrib/admin -->
<a href="{% url 'admin:shop_product_changelist' %}">Admin products</a> <!-- automatic url from contrib/admin -->
Refresh your 127.0.0.1:8000 to see our first ever page:
Play around with the ORM in the Django shell
Django provides a very helpful way to debug and try things with the django shell. Invoke it with the shell command:
$ ./manage.py shell
Python 3.7.2...
>>> from shop.models import Product
>>> Product.objects.all()
<QuerySet []>
>>> p = Product(name="Pen"); p.save(); p.id # 2-steps creation
1
>>> Product.objects.create(name="Car", notation=5) # 1-step creation
>>> Product.objects.create(name="Mac", description="Better than a PC")
>>> Product.objects.all()
<QuerySet [<Product: Product Pen(1)>, <Product: Product Car(2)>, <Product: Product Mac(3)>]
>>> Product.objects.filter(name__contains='a') # double underscore field lookup, see https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.1/topics/db/queries/#field-lookups-intro
>>> Product.objects.filter(notation__gte=5) # greater than or equal
<QuerySet [<Product: Car(2)>]>
<QuerySet [<Product: Product Car(2)>, <Product: Product Mac(3)>]
>>> Product.objects.filter(description__endswith='PC').count() # chainable API
1
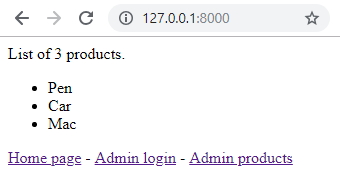
Refresh 127.0.0.1:8000 and see the updated list of products:
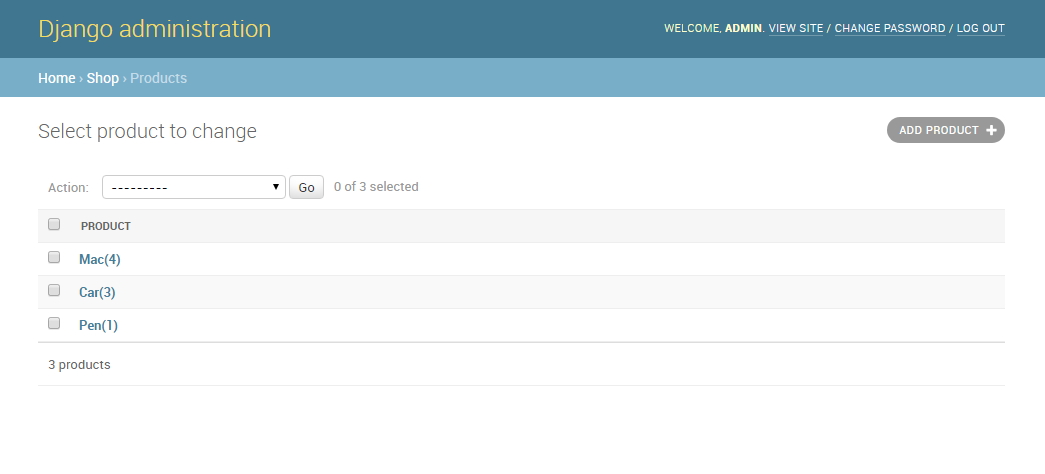
As well as the administration Products list:
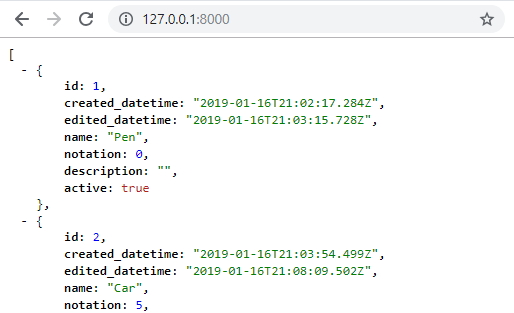
Output JSON for API purposes
Let’s say we would like our index page to output application/json. Start by editing shop/views.py:
def get(self, request):
products = list(map(lambda x: x.as_dict(), Product.objects.filter(active=1))) # as_dict is defined below
return JsonResponse(products, safe=False)
And add as_dict() in shop/models.py:
def as_dict(self):
d = self.__dict__
del d['_state']
return d